Location Results
- Figures 1 and 2 show the location means at sampled locations across Southwestern Ontario in 2022 and 2023, respectively, where location mean DON level was greater than 0.25 ppm.
- Disease severity in 2022 was low overall, but individual fields were still moderately affected by Gibberella ear rot. The mean location average was 1.56 ppm, and the highest location average was 9.4 ppm. The highest reported DON across all locations and hybrids was 17.8 ppm.
- Disease incidence and severity of Gibberella ear rot in 2023 was higher. The mean location average in 2023 was 2.9 ppm. The highest location average was 10.2 ppm, while the highest reported DON across all locations and hybrids was 30.2 ppm.
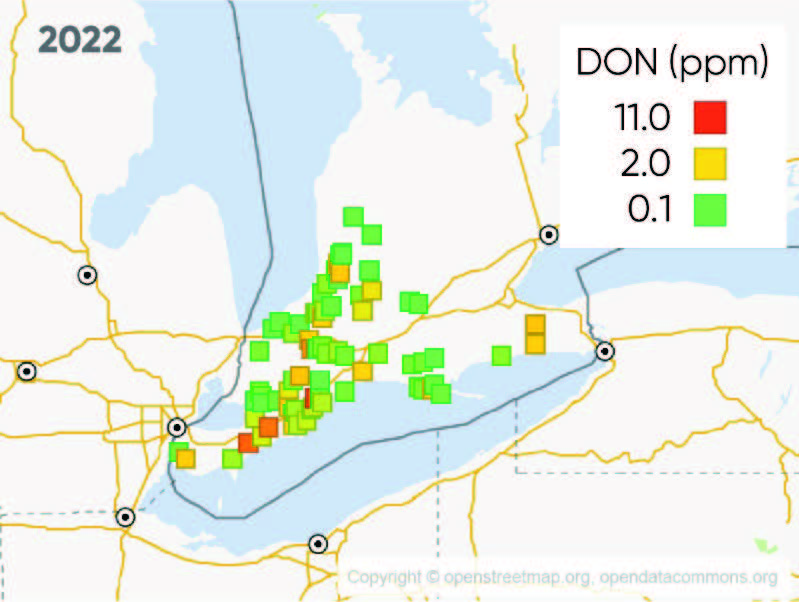
Figure 1. Location mean DON levels (ppm) at 2022 sampling sites.
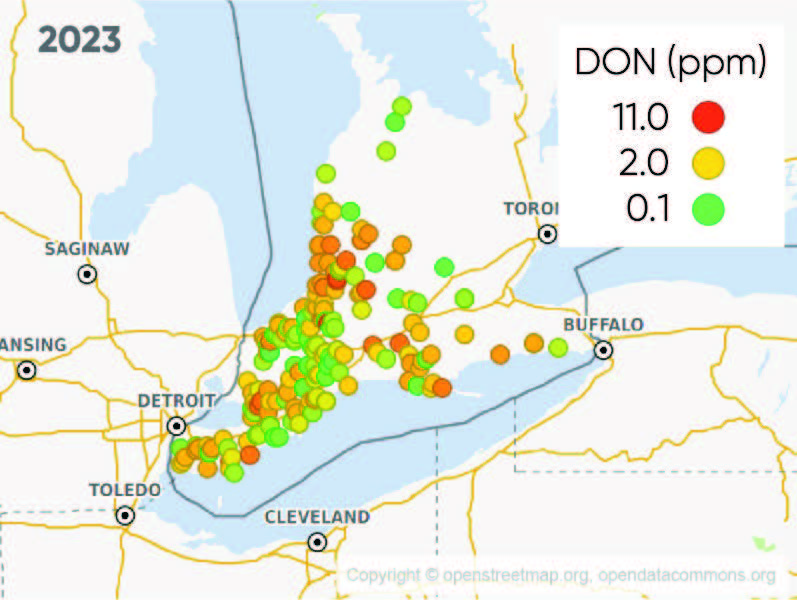
Figure 2. Location mean DON levels (ppm) at 2023 sampling sites.
Table 1. Average DON level by corn hybrid as a percentage of location mean across 2022 and 2023 sampling sites, total number of locations sampled, and hybrid Gibberella ear rot trait score.
Pioneer Brand Product1
|
DON
Average (% of location mean)
|
n
|
Gibberella Trait Score (1-9)
|
P0075Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
41.4%
|
88
|
6
|
P0306Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
48.0%
|
9
|
4
|
P0035Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
48.2%
|
161
|
5
|
P9624Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
48.7%
|
51
|
7
|
P9233Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
51.8%
|
15
|
5
|
P0806AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
52.0%
|
65
|
4
|
P9823Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
54.9%
|
94
|
5
|
P0720Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
59.0%
|
85
|
4
|
P9316Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
63.7%
|
16
|
6
|
P0075AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
67.2%
|
67
|
6
|
P9998Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
68.6%
|
5
|
4
|
P9845AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
72.5%
|
44
|
4
|
P0404AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
73.9%
|
33
|
5
|
P0506AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
74.0%
|
17
|
5
|
P0157AMXT™ (AMXT,LL,RR2)
|
78.9%
|
10
|
4
|
P0035AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
80.4%
|
66
|
5
|
P0306AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
83.3%
|
10
|
4
|
P1136AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
84.2%
|
22
|
6
|
P87040AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
84.3%
|
4
|
|
P9466AML™ (AML,LL,RR2)
|
84.7%
|
43
|
5
|
P0404Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
85.4%
|
79
|
5
|
P0529Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
87.5%
|
161
|
5
|
P9026AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
107.1%
|
14
|
|
P9845PCE™ (PW,ENL,RIB)
|
112.2%
|
45
|
4
|
P9946AML™ (AML,LL,RR2)
|
121.3%
|
13
|
6
|
P04511AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
124.1%
|
97
|
4
|
P9535AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
126.4%
|
33
|
4
|
P0720AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
127.9%
|
43
|
4
|
P0859AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
139.0%
|
41
|
3
|
P04922Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
|
143.8%
|
70
|
3
|
P97299AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
164.6%
|
63
|
3
|
P9998AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
185.2%
|
5
|
4
|
P1197AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
215.5%
|
6
|
5
|
P0953AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
235.5%
|
56
|
3
|
P0487Q™ (Q,LL,RR2)
P8859AM™ (AM,LL,RR2)
|
236.3%
242.5%
|
72
4
|
3
|
1All Pioneer products are hybrids unless designated with AM, AML, AMT, AMX, AMXT, Q, V, PCE, PCUE, PWE & PWUE, in which case they are brands.
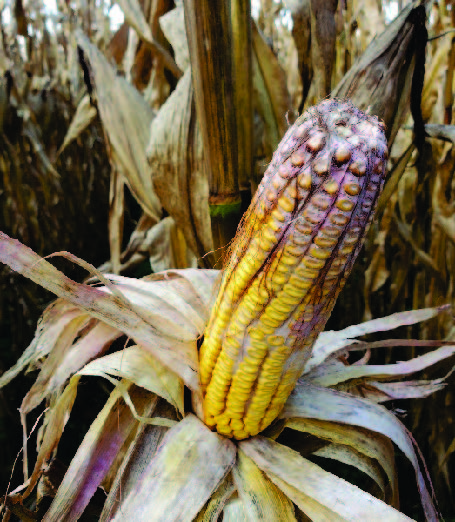

Figure 3. Gibberella zeae, the fungal pathogen that causes Gibberella ear rot, can produce the mycotoxin deoxyni- valenol (DON). Gibberella ear rot can be most readily identified by the red or pink color of the mold.
Hybrid Results
- Across years, 162 unique hybrids were evaluated. Results are reported for 36 Pioneer® brand corn products for which more than four samples were collected. DON accumulation is reported for each hybrid as a percent of the location mean. (Table 1).
- Across years, DON accumulation by hybrid – as a percentage of the location average – ranged from 41% to 243%.
- The results, expressed as a percentage of the location average, provide an indication of relative risk of DON accumulation under 2022 and 2023 environmental conditions. In many cases, hybrids that had above-average DON levels relative to the location average were still low in absolute terms.
- Pioneer brand corn products are rated for genetic resistance to Gibberella ear rot. Each rating is backed by thousands of research hours and on-farm trials. Trait scores range from 1 (most susceptible) to 9 (most resistant).
- Trait scores for Gibberella ear rot range from 3 to 7 for current Pioneer brand corn products, illustrating that – while there is no complete resistance for Gibberella ear rot – significant genetic differences do exist.
- Hybrid results in this study were consistent with both anecdotal and research experience, where hybrids with a Gibberella ear rot trait score of 4 or less tended to have higher levels of DON.











